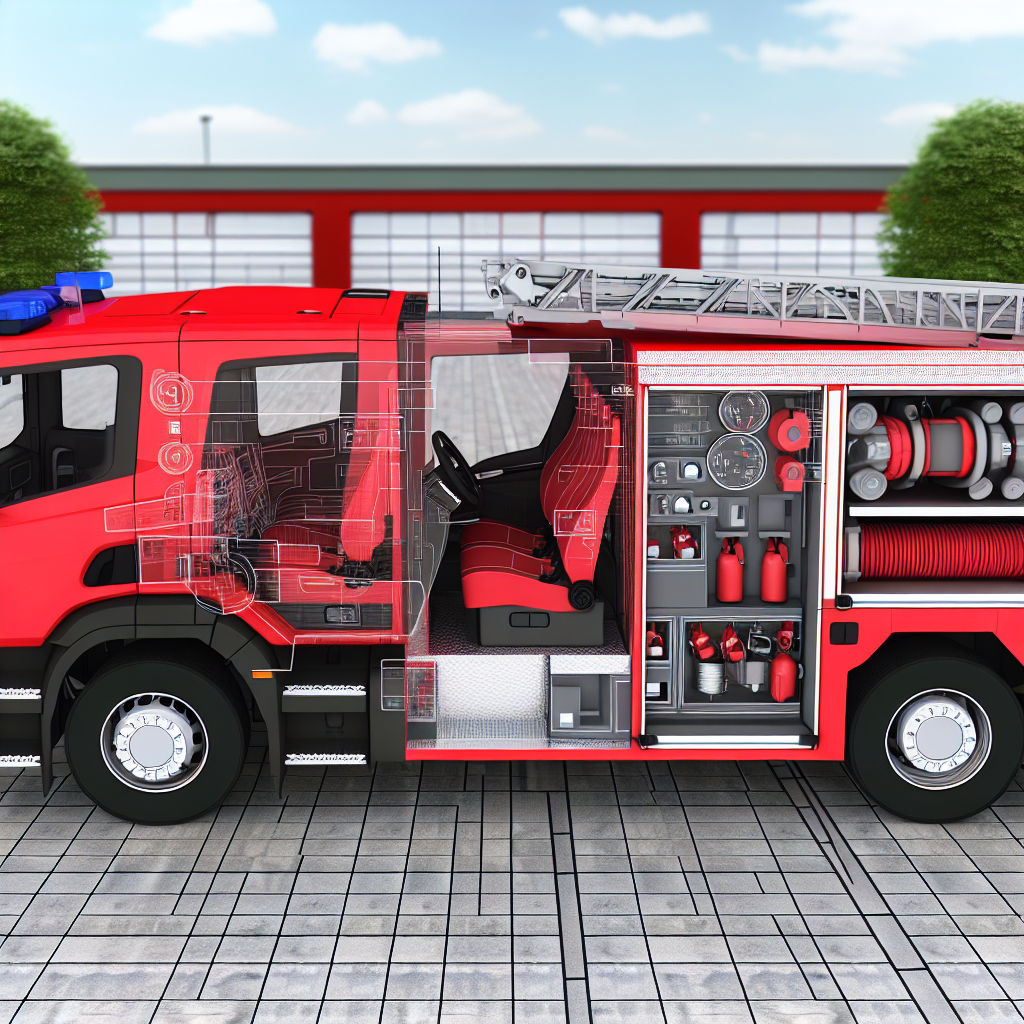
When seconds count, the effectiveness of emergency response teams relies heavily on the design of their equipment, particularly pumper fire trucks. These vehicles are not merely mechanical giants; they are lifelines that can impact life and death. Safety and ergonomic design play a significant role in ensuring firefighters can operate with precision, especially during high-pressure situations.
Innovations in pumper fire truck design enhance safety, streamline operations, and optimize performance in chaotic circumstances. Thoughtful considerations like the placement of controls and accessibility to tools can significantly enhance safety for both firefighters and civilians. As we explore the essential features of modern pumper fire trucks, every detail in their design will demonstrate its contribution to operational efficiency and the ultimate protection of those involved.
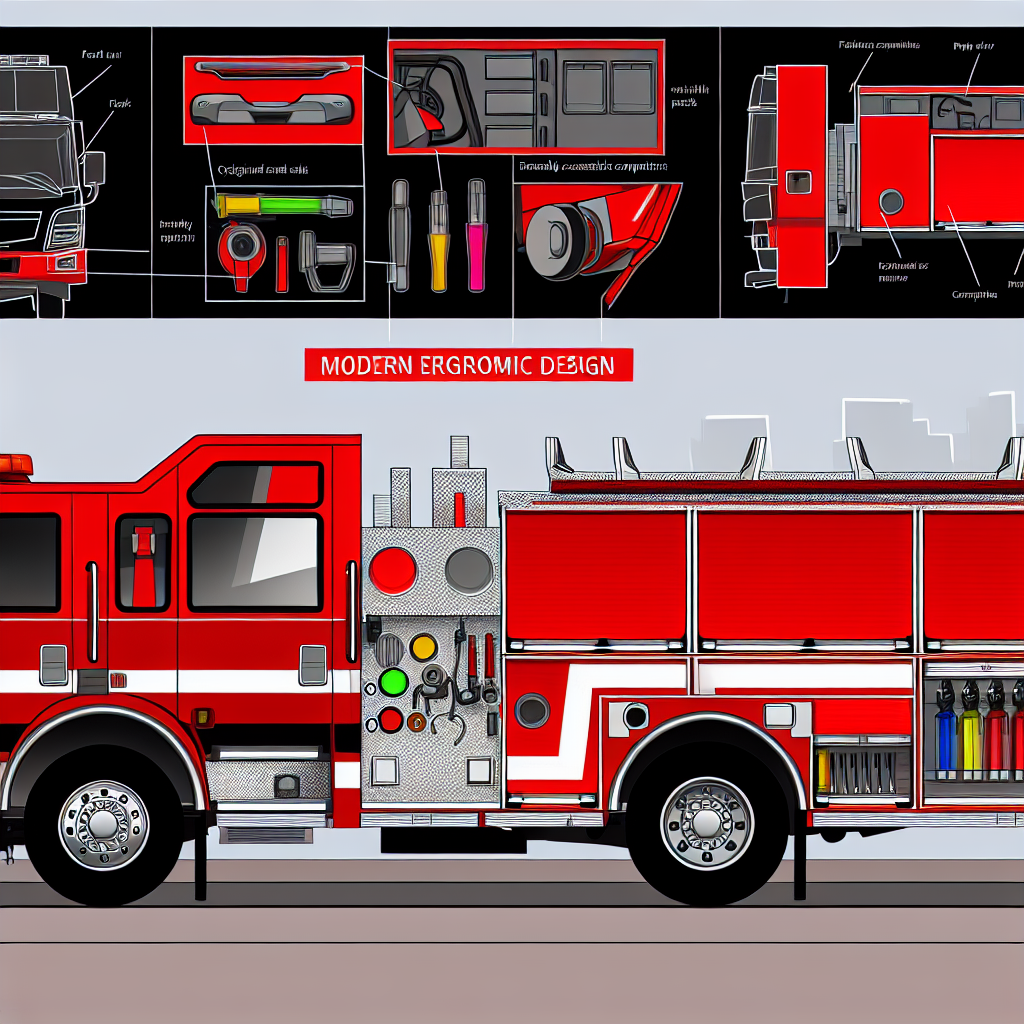
The Importance of Ergonomics in Fire Truck Design
Ergonomics plays a crucial role in the design of pumper fire trucks, especially concerning the safety and efficiency of firefighters in high-pressure situations. Key features such as adjustable hose beds and easily accessible storage compartments significantly contribute to reducing physical strain, which is paramount in the demanding environments that firefighters operate in.
One of the primary ergonomic features is the adjustable hose bed, which allows firefighters to configure the hose at an optimal height relative to their physical capabilities. This customization minimizes unnecessary bending and reaching, which can lead to musculoskeletal injuries. When hose beds are set at the right level, it becomes easier for firefighters to pull hoses quickly and efficiently, saving precious seconds during an emergency. This not only enhances personal safety but also positively impacts overall team effectiveness in late-stage strategies during crises.
In addition to hose adjustability, accessible storage compartments are vital in modern pumper fire trucks. These compartments are designed to hold tools, equipment, and personal protective gear, organized in a way that allows for rapid retrieval. When emergency scenarios unfold, every second counts, so firefighters benefit immensely from compartments that can be opened decisively, without the need to struggle or dig through cluttered spaces. Properly designed storage systems not only facilitate quick access to necessary tools but also ensure that equipment is securely stowed when the vehicle is in motion, consequently enhancing safety during transport.
Moreover, these ergonomically designed features translate into a significant reduction in fatigue levels among firefighters. Exhaustion can lead to mistakes and slower response times, so a design that aids in maintaining physical well-being is intrinsically linked to operational efficiency. A fire truck that incorporates ergonomic elements allows firefighters to operate at their best, which ultimately protects not only the firefighters but also the communities they serve.
In conclusion, the integration of ergonomic features in fire truck design, particularly through adjustable hose beds and accessible storage compartments, is essential for maximizing firefighter performance, safety, and operational efficiency. Investing in such thoughtful designs is a crucial step towards protecting those who bravely risk their lives to save others.
| Feature | Pierce Manufacturing | Oshkosh Corporation |
|---|---|---|
| Tank Size | 500 to 1,000 gallons | Typically 1,000 gallons (e.g., Striker ARFF) |
| Hose Bed Height | 74 inches (low design) | N/A (focus on ARFF vehicles) |
| Water Capacity | Customizable sizes ranging up to 1,000 gallons | 1,000 gallons (ARFF vehicles) |
| Ergonomic Controls | Transverse compartment for tools | Color-coded controls, improved visibility |
| Seating | Standard cab designs, adjustable positions | Spacious seating for up to five firefighters |
| Safety Features | Slide-out trays, better hose access | TAK-4® all-wheel independent suspension, airbags |
| Clean Options | Regular wash capabilities | Cleanable surfaces and optional wash stations |
User Adoption of Ergonomic Enhancements in Fire Truck Designs
Recent advancements in fire truck design have increasingly focused on ergonomic enhancements aimed at improving firefighter safety and operational efficiency. While specific user adoption data is limited, several developments highlight the integration of ergonomic features and their impacts on fire departments’ operational capabilities:
- Ergonomic Seating and Seatbelt Design: A study published in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene emphasizes the need for fire apparatus seating and seatbelt systems that accommodate firefighters’ protective gear and diverse body sizes. The research suggests specific dimensions for seat components to enhance comfort and safety, including a seat pan width of 498 mm and a seat backrest height of 542 mm. Implementing these ergonomic designs can reduce fatigue and injury risk, thereby improving operational performance. Source
- Fleet Standardization and Ergonomic Equipment Storage: The Prince George’s County Fire/EMS Department has adopted standardized fleet designs featuring advanced apparatus with ergonomic equipment storage systems. These systems are designed to store equipment efficiently in tight spaces while ensuring easy access, positioning heavy items lower to reduce strain. Such ergonomic enhancements have led to improved mechanical consistency, reduced diagnostic and repair times, and enhanced response capabilities, as evidenced by over 1,800 emergency responses in 2024. Source
- Technological Integration for Enhanced Safety: Modern fire trucks are incorporating technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and infrared (IR) vision systems to assist drivers in low-visibility conditions. These systems enhance navigation and situational awareness, contributing to safer and more efficient operations. For instance, IR cameras can detect thermal signatures of obstacles, improving driver safety during nighttime or foggy conditions. Source
- Ergonomic Design in Military Fire Trucks: The Air Force has introduced fire trucks with ergonomic designs that improve firefighter communication and efficiency. Features include seating arrangements that position firefighters opposite each other to foster better coordination, low entry heights, and adjustable settings to accommodate various body sizes. These design enhancements, developed with user input, ensure the vehicles meet operational demands effectively. Source
While comprehensive statistical data on the adoption rates of these ergonomic enhancements is scarce, these examples illustrate a growing trend towards integrating ergonomic features in fire truck designs. These improvements aim to enhance firefighter safety, reduce physical strain, and improve overall operational efficiency within fire departments.
As James Curtis noted, “…every decision, from hosebed height to tank size, directly affects on-scene performance.” This statement reinforces the importance of thoughtful design in fire truck engineering. In modern fire truck design, ergonomics and practical layout not only support safe operations but also significantly enhance response times and operational efficiency. Ergonomically designed controls and accessible equipment storage allow firefighters to deploy necessary tools swiftly, which can be life-saving in emergency situations. Incorporating these principles into pumper fire truck design is essential for maximizing both safety and effectiveness.
Key Features Fire Departments Should Prioritize in Pumper Fire Truck Design
Designing an effective fire truck involves careful consideration of several key features to ensure optimal performance during emergency operations. These features include pump ratings, water capacity, and gear storage, each tailored to meet the specific needs of fire departments.
Pump Ratings
The pump system is central to a fire truck’s functionality, determining its ability to deliver water at required pressures. Pump capacities typically range from 500 to 3,000 gallons per minute (GPM), depending on the department’s operational demands. For instance, departments handling high-volume fire incidents or operating in areas with limited water supply may opt for pumps with higher capacities to maintain adequate flow and pressure. Multi-stage pumps, such as two-stage models, offer flexibility by allowing crews to switch between high-pressure and high-volume modes, particularly beneficial for high-rise operations or extended hose lays.
Water Capacity
The size of the onboard water tank directly impacts the duration a crew can combat a fire before establishing a hydrant connection. Standard tanks typically hold around 750 gallons, balancing space, weight, and sustained water flow. In regions with limited hydrant access, larger tanks can be crucial. For example, the South County Fire Department increased their tank capacity beyond the standard 500 gallons after data revealed they ran out of water in nearly 30% of incidents before securing a hydrant connection.
Gear Storage
Efficient storage solutions are vital for quick access to firefighting equipment. Organized, accessible compartments support operational efficiency and safety. Features like low ladder mounts, swing-out tool boards, and slide-out trays facilitate faster and safer equipment retrieval. The South County Fire Department streamlined their equipment inventory, focusing on critical tools to reduce clutter and lighten the overall load, resulting in a more intentional and task-driven layout.
In summary, tailoring pump ratings, water capacity, and gear storage to a fire department’s specific operational needs enhances the effectiveness and safety of fire trucks during emergency responses.
In conclusion, the design of pumper fire trucks represents a critical intersection of safety, ergonomics, and operational effectiveness. As we have explored throughout this discussion, the thoughtful integration of ergonomic features—such as adjustable hose beds, accessible storage compartments, and innovative control layouts—has significant implications for the safety and performance of firefighters in high-pressure situations. By minimizing physical strain and facilitating rapid access to tools, fire departments can ensure that their personnel can respond swiftly and efficiently, ultimately making a difference during emergencies. Additionally, the emphasis on safety features not only protects firefighters but also enhances their capability to serve and protect communities.
As emphasized by industry experts, every decision regarding the design of fire trucks must consider the impact on operational efficiency. The advancements in pumper fire truck design underscore the importance of prioritizing ergonomic principles to protect those who risk their lives for others. Consequently, as fire departments evaluate their fleet designs moving forward, they must embrace these principles as essential components in their quest to maximize the effectiveness of their emergency response operations. Investing in safer and more ergonomic pumper fire trucks translates not just into better equipment, but ultimately into saved lives and enhanced community safety.
Understanding Pump Ratings and Their Importance
Fire truck pump ratings, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 gallons per minute (GPM), are crucial in determining a fire apparatus’s ability to deliver water effectively during firefighting operations. Higher pump capacities enable fire departments to manage larger fires and supply multiple hose lines simultaneously, thereby enhancing firefighting efficiency.
Pump Performance Standards
The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets performance standards for fire pumps to ensure reliability under various conditions. For instance, NFPA 1911 outlines that fire pumps with capacities between 250 GPM and 3,000 GPM must undergo rigorous testing:
- Operate at 100% of rated capacity at 150 psi for at least 20 minutes.
- Operate at 70% of rated capacity at 200 psi for at least 10 minutes.
- Operate at 50% of rated capacity at 250 psi for at least 10 minutes.
These tests ensure that pumps can perform effectively under the pressures encountered during firefighting operations. [source]
Impact on Firefighting Efficiency
The pump’s capacity directly influences a fire department’s operational capabilities:
- 500 to 750 GPM Pumps: Suitable for smaller residential fires, these pumps can handle one or two hose lines effectively.
- 1,000 to 1,500 GPM Pumps: Common in urban settings, they provide sufficient water flow for moderate-sized fires and can support multiple hose lines.
- 2,000 to 3,000 GPM Pumps: Designed for large-scale incidents, such as industrial fires or high-rise buildings, these high-capacity pumps can supply extensive hose operations and master streams.
For example, a fire pump rated at 1,250 GPM can deliver enough water to control a fire involving approximately 3,750 square feet, based on the National Fire Academy’s fire flow formula. This calculation underscores the importance of matching pump capacity to the potential fire load to ensure effective suppression. [source]
Considerations for Fire Departments
When selecting fire apparatus, departments must assess their community’s specific needs, including building types, population density, and potential fire hazards. Ensuring that pump capacities align with these factors is vital for maintaining optimal firefighting efficiency and safety.
In summary, understanding and appropriately selecting fire truck pump ratings are fundamental to a fire department’s ability to respond effectively to various fire scenarios, thereby safeguarding lives and property.
User Experience Facts Regarding Water Tank Sizes and Firefighting Efficiency
The history of firefighting has demonstrated the critical importance of water availability during emergency responses. For example, in the South County Fire Department, statistics reveal that they ran out of water in nearly 30% of incidents before the establishment of hydrants. This alarming trend underscores how essential it is for fire trucks to have appropriately sized water tanks.
Key insights into the relationship between tank sizes and operational efficiency include:
- Water Tank Sizes: Fire trucks typically carry between 500 to 1,000 gallons in urban settings, while rural tankers often hold 1,500 to 3,000 gallons. This variance allows departments to tailor their equipment to the specific challenges they face in their service areas. source
- Operational Impact: Larger tanks not only provide a more substantial water supply but also enhance firefighting capabilities in initial response phases. Conversely, smaller tanks can lead to more frequent refills and slower response times, potentially compromising the effectiveness of firefighting efforts. source
- Lessons from Past Incidents: During the January 2025 Southern California wildfires, historical data highlighted how quickly tank supplies can deplete. In densely populated areas, multiple tanks were drained, resulting in significant challenges for firefighters responding to devastating flames and leading to the loss of over 1,000 structures. source
- Advancements in Technology: With technologies like Compressed Air Foam Systems (CAFS), a smaller fire truck can achieve similar effectiveness to larger counterparts. For instance, a fire truck equipped with a 500-gallon tank can perform comparably to one with a 2,500 to 5,000-gallon tank by using foam to extend the reach of water in critical situations. source
In conclusion, tank sizes pose critical implications for fire departments’ ability to respond effectively in emergencies. The operational readiness and safety of firefighting teams are directly influenced by the capacity and maintenance of fire truck water tanks. Thus, designing fire trucks with adequate tank sizes is important for enhancing efficiency and ensuring successful fire suppression efforts.
Integrating Personal Anecdotes from Firefighters
Integrating personal anecdotes from firefighters can provide relatable insights into pumper fire truck design. Here are some noteworthy experiences that highlight issues encountered and solutions provided by modern pumper design:
Ergonomic Features
Firefighters consistently share how modern ergonomic designs have improved their efficiency and safety. For instance, one firefighter recounted a late-night call where they needed to quickly access hoses and tools during a high-pressure situation. Thanks to the Pierce Ultimate Configuration (PUC), which positions the pump below the cab and features chest-high crosslays, they were able to pull hoses without straining their backs. This design allows firefighters to operate quickly and comfortably, reducing wear and tear during demanding calls.
Water Tank Capacities
The importance of adequate water supply cannot be overstated. A firefighter from South County Fire shared their experience regarding how the increase in their water tank size from 500 gallons significantly impacted their operations. In earlier incidents, their team often faced daunting situations due to running out of water before being able to connect to a hydrant. With the new tanks capable of carrying more water, they were able to manage emergencies more effectively, providing cohesive support that ultimately saved lives during critical moments.
Pump Ratings
Another firefighter emphasized the critical nature of pump ratings by sharing a story from a large-scale fire involving multiple structures. Their pumper truck was equipped with a high-capacity pump rated for 2,500 gallons per minute, allowing their crew to supply extensive hose lines while supporting rapid fire suppression. This capacity proved essential in managing the situation efficiently and coordinating their firefighting efforts across several locations simultaneously.
These personal experiences underscore the pronounced benefits of modern pumper fire truck design elements, such as ergonomic enhancements, adaptable water tank sizes, and adjustable pump ratings. As firefighters navigate the challenges faced during emergencies, the role of thoughtful design becomes clearly evident in improving operational efficiency and ensuring their safety.
When seconds count, the effectiveness of emergency response teams relies heavily on the design of their equipment, particularly pumper fire trucks. These vehicles are not merely mechanical giants; they are lifelines that can impact life and death. Safety and ergonomic design play a significant role in ensuring firefighter safety and operational efficiency, especially during high-pressure situations.
Innovations in pumper fire truck design not only enhance safety but also streamline operations and optimize performance in chaotic circumstances. Thoughtful considerations like the placement of controls and accessibility to tools can significantly improve not only firefighter safety but also the serviceability of the fire truck. As we explore the essential features of modern pumper fire trucks, every detail in their design will demonstrate its contribution to operational efficiency and the ultimate protection of those involved.
Enhanced Narrative Flow
The article presents a well-structured journey from understanding the critical role that pumper fire trucks play in emergency response to the specific features that enhance their effectiveness. To improve the flow of the narrative, the following enhancements to transitions between key sections are proposed:
- Connecting the Introduction and Ergonomics Section: When we discuss why safety and ergonomics are paramount in fire truck design, we can include a statement that emphasizes how these aspects directly impact operational efficiency. A transition could read, “As we delve deeper, it becomes evident that the design features, particularly ergonomic elements, are integral to ensuring that firefighters can navigate high-pressure situations effectively.”
- Bridging Ergonomics and Features Comparison Table: After highlighting the importance of ergonomics, linking this to the features comparison can be made more cohesive. For example, stating, “The insights gained from ergonomic design lead us to assess how various manufacturers implement these principles in their fire truck offerings, as showcased in the following comparison table.”
- Transition from Features Comparison to User Adoption: After discussing the comparative features, it’s vital to connect those to real-world application and adoption by fire departments. Incorporate a transition such as, “These features are not just theoretical; they have practical implications, as seen in the growing adoption of ergonomic enhancements by numerous fire departments in the field.”
- Recap in the Conclusion: In the conclusion, reiterate how the discussions reflect back on the introduction’s emphasis on safety. Including a sentiment like, “Ultimately, the integration of thoughtful design choices in fire truck engineering represents our commitment to safeguarding those who risk their lives to save others, echoing our earlier discussion on the life-or-death stakes involved.”
These targeted transitions serve to weave the sections together, enhancing comprehension and reinforcing the critical relationship between design choice and operational effectiveness. The proposed enhancements will strengthen the narrative structure, guiding the reader seamlessly through the article’s key points.

